
Remote Terminal Unit
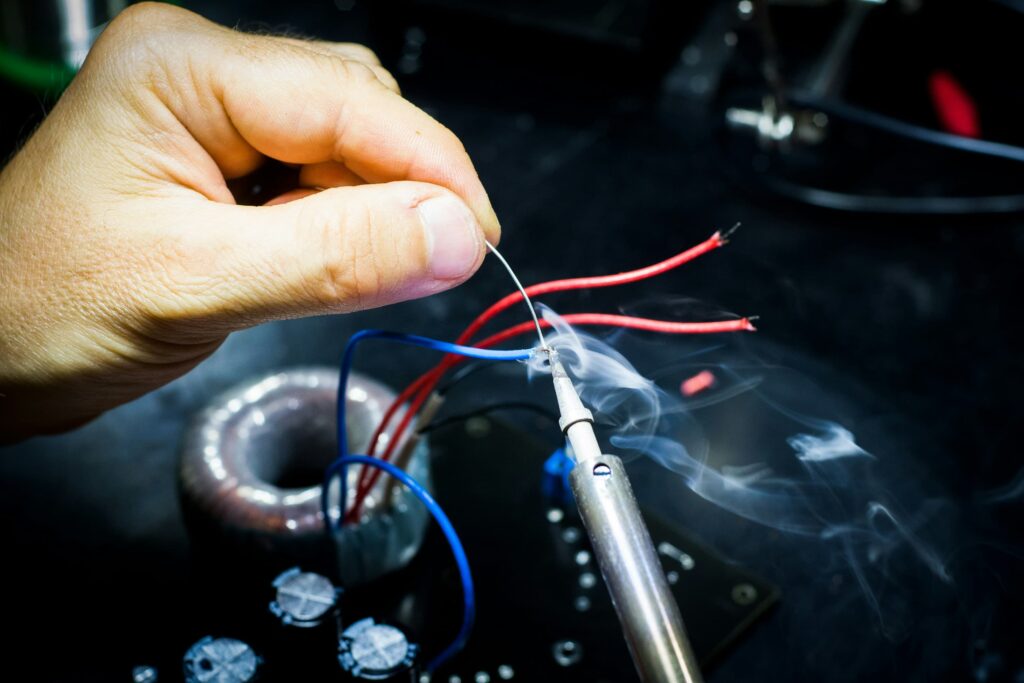
Overview
A Remote Terminal Unit (RTU) is a microprocessor-based device used for remote monitoring and control of industrial equipment and systems. RTUs are commonly used in various industries, including utilities, oil and gas, water and wastewater, and environmental monitoring, to collect data from field devices, transmit it to a central system, and execute control commands.
Key Features
Modbus Protocol Support: Compatible with Modbus RTU and Modbus TCP protocols for seamless integration with existing industrial systems and equipment.
Wi-Fi Connectivity: Built-in Wi-Fi capability allows for wireless communication, enabling remote monitoring and control without the need for physical network connections.
SIM-Based Connectivity: Equipped with SIM card support for cellular communication, ensuring reliable data transmission in remote or mobile applications where Wi-Fi or wired networks are unavailable.
Multi-Channel I/O: Multiple input and output channels to interface with a wide range of sensors and actuators, including analog, digital, and pulse inputs/outputs.
Data Logging: Internal storage for logging data locally, ensuring data is recorded even if communication is temporarily lost.
Real-Time Monitoring: Provides real-time data acquisition and monitoring, enabling timely response to changing conditions.
Rugged Design: Built to withstand harsh industrial environments, with robust enclosures and protection against dust, moisture, and temperature extremes.
User-Friendly Interface: Intuitive web-based interface for easy configuration, monitoring, and management of the RTU.
Applications
Utilities: Monitoring and controlling electrical substations, water treatment plants, and gas pipelines.
Oil and Gas: Managing remote wellheads, pipelines, and distribution networks.
Water and Wastewater: Supervising pump stations, water reservoirs, and wastewater treatment facilities.
Environmental Monitoring: Tracking environmental parameters such as air and water quality, weather conditions, and soil moisture.
Industrial Automation: Integrating with SCADA systems for process control and automation in manufacturing plants.
Benefits
Enhanced Connectivity: Flexible communication options (Wi-Fi and cellular) ensure reliable data transmission in diverse environments.
Scalability: Easily expandable to accommodate additional sensors and control points as your system grows.
Cost-Effective: Reduces the need for extensive cabling and infrastructure, particularly in remote or hard-to-reach locations.
Improved Decision Making: Provides real-time data and remote control capabilities, facilitating informed decision-making and rapid response to issues.
Increased Reliability: Ensures continuous data logging and robust communication, even in challenging conditions.
How It Works

Setup
Install the RTU at the desired location and connect it to the required sensors and actuators.

Configuration
Use the web-based interface to configure the RTU settings, including network parameters, data logging intervals, and Modbus communication.
Data Collection
The RTU collects data from connected field devices and logs it locally.
Data Transmission
Transmit the collected data to a central SCADA system or cloud-based platform using Wi-Fi or cellular connectivity.

Remote Control
Execute control commands from the central system to the RTU, enabling remote operation of connected equipment.


